
IN KAZAKHSTAN

Legal and regulatory framework for dual education in the Republic of Kazakhstan
In the regulatory framework of the Republic of Kazakhstan, dual education is reflected in a number of documents.
The Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On Education” dated July 27, 2007, article 1, paragraph 19-1, defines dual training as a form of training that combines training in an educational organization with mandatory periods of industrial training and professional practice at an enterprise (in an organization) with providing jobs and compensation payments to students with equal responsibility of the enterprise (organization), educational institution and student [22].
This provision is enshrined in the Labor Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated November 23, 2015 No. 414-V ZRK, chapter 9, article 119, where it is indicated that dual training is carried out in accordance with a model contract, which is approved by the authorized body in the field of education. During the period of industrial training and professional practice, the student is subject to labor regulations, safety and labor protection requirements. In addition, during the course of industrial training and professional practice, the student is credited with work experience, and compensation payments can be made. Thus, the student is practically equated to the worker. Also, on the basis of an agreement on dual training, a mentor is assigned to the student [23].
The SES of higher education (Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 604 chapter 2, paragraph 20) states that universities that introduce elements of a dual education system plan and organize educational activities based on a combination of theoretical training with practical training at work. [24].
According to paragraph 19 of the State Educational Standard of the Republic of Kazakhstan in 2022, organizations of higher and postgraduate education that introduce elements of the dual training system carry out planning and organization of educational activities based on a combination of theoretical training with practical training at work. At the same time, it is necessary to master at least 30% of the educational material of the discipline directly in production (the technological process, the process of creative activity, financial and economic processes, the psychological and pedagogical process) [25]. In our opinion, this provision requires clarification and additional clarifications, since it has an ambiguous interpretation of the norm "at least 30% of the educational material of the discipline to master directly at work" and does not specify the profile of the discipline.
Chapter 2 of the State Educational Standard “Requirements for the content of technical and vocational education with a focus on learning outcomes” notes that TVE educational programs, along with theoretical training, provide for industrial training and professional practice. Professional practice in TVE is divided into educational, industrial and pre-diploma. The terms and content of industrial training and professional practice are determined by the plan of the educational process and working training programs.
The rules for organizing dual education (Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated January 21, 2016 No. 50) apply to educational institutions implementing educational programs of technical and vocational, post-secondary education, regardless of the form of ownership and departmental subordination, training centers, enterprises (organizations) participating in dual education [ 1].
Based on the analysis and review of the regulatory framework of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the project team summarized various approaches to the definition of “dual education” and proposed a working conceptual and terminological apparatus used in this work and indicated in the Basic Concepts section. (Table 1.1).
Table 1.1 - Approaches to the definition of dual learning
|
№ |
concept |
Definition |
|
1 |
Elements of the dual learning |
- increase in the volume of hours for practical classes and production (pedagogical) practice; wider introduction of practice-oriented learning technologies. |
|
2 |
Dual training |
- a form of personnel training that combines training in an educational organization with mandatory periods of industrial training and professional practice at an enterprise (in an organization) with the provision of jobs and compensation payments to students with equal responsibility of the enterprise (organization), educational institution and student (LRK "On Education") |
|
3 |
Dual education (working definition of the Project team) |
- an integral system of theoretical and practical training of qualified personnel with the prevalence of practice-oriented training based on the order of the enterprise (organization), in which employers are directly involved in the development of educational programs, in providing students with mentors, and in their final certification to form the professional competencies of students in the workplace . |
|
4 |
Dual education system (working definition of the Project team) |
- an integral system of personnel training on the corporate order of an enterprise (organization) that is directly involved in updating educational programs, appoints mentors from among specially trained specialists, and takes the final demonstration exam. Based on the results of this exam, a decision is made on employment and further career in the enterprise. |
General overview of the state of dual education in Kazakhstan:
coordination, contingent, coverage of regions
The introduction of a dual education system in technical and vocational education organizations of the Republic of Kazakhstan began in 2012. Initially, 25 colleges of the Republic of Kazakhstan took part in a pilot project to introduce a dual education system, then their number grew continuously. According to the "National Report - 2020" [22], the number of enterprises and companies with which contracts were concluded for training personnel in the framework of dual training amounted to 5,507 units. At the same time, the share of students studying under the state order, covered by dual training, was only 18.6%. The highest enrollment rates for dual education were recorded in Zhambyl and Pavlodar regions and amounted to 38% and 28% respectively. Figure 1.1 shows the results of monitoring the coverage of college students with dual education by regions according to 2020 data.
The share of students studying under the state order, covered by dual education
by regions, 2020, %
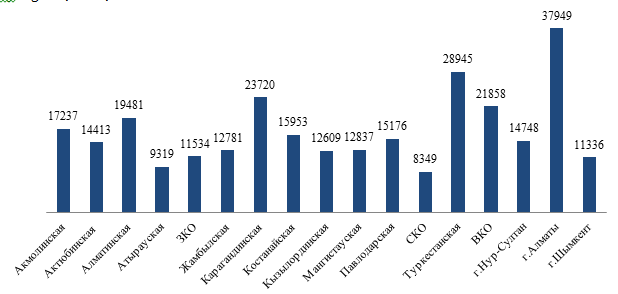
Figure 1.1 - Coverage of college students with dual education by regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan (https://iac.kz/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/naczionalnyj-doklad-po-itogam-2020-goda.pdf)
An important role in the planning, implementation and coordination of dual education in the TVET system is played by the National Chamber of Entrepreneurs of the Republic of Kazakhstan "Atameken". The Chamber of Entrepreneurs represents the interests of small, medium and large businesses, covers all areas of business and advocates for the active involvement of Kazakhstani businesses in the implementation of state programs, an important part of which is the training of specialists, employment of young people and the implementation of socially significant projects.
Thus, with the assistance of NCE RK "Atameken", the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On Education" included the terms "mentor", "industrial training", competencies of stakeholders for the development of dual training, and so on.
The Labor Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan introduced the concepts of “dual training”, “dual training agreement”, as well as a new article “Dual training” (Article 119). The rules for the organization of dual training (Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated January 21, 2016 No. 50) were also developed jointly with NCE RK "Atameken". The main planning documents of the country for the development of dual education were the Roadmaps for the implementation of the dual education system, adopted in 2014 and 2019. They are implemented in priority sectors, 99 specialties and 152 qualifications.
The successful promotion of dual programs in Kazakhstan is facilitated by such a form of partnership as training and production consortia, examples of which are the consortium of the Association of Service and Service Entrepreneurs and the Kyzylorda Industrial and Technical College (Kyzylorda region) and the consortium of Kazphosphate LLP and the Taraz Chemical-Technological College ( Jambyl Region).
At the beginning of the 2021/2022 academic year, there are 724 colleges in Kazakhstan, and there are 38 TVET branches. They have 719 full-time, 14 evening and 287 correspondence departments. The total number of students is 493.3 thousand people. Of these, according to the NCE RK "Atameken", 55,127 college students became participants in dual training (Fig. 1.2). Similar statistical data can be found in the National reports on the state and development of the education system of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
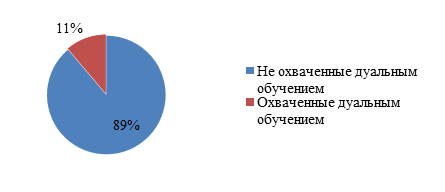
Total: 433.3 thousand college students
Of these, covered by dual training - 11% (55127)
Figure 1.2 - Share of students enrolled in dual education out of the total number of students in the TVET system (https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=39706228)
The employment rate for the period under review increased to 85%, in contrast to traditional education (60-65%), which indicates the effectiveness of the dual form of education [26].
According to the NCE RK "Atameken", in the TVE system, both the number of students in the dual model and enterprises implementing dual training are growing annually (Fig. 1.3). As of 2021, 4114 enterprises are involved as partners in dual training, however, as a percentage of the total number of enterprises and companies in Kazakhstan, the share of companies covered by dual training remains low. This actualizes the involvement of more enterprises (organizations) for the implementation of dual training.
Introduction of dual training (implementation of the dual training roadmap)
Dual education coverage 55127 students, 4114 enterprises, 473 colleges
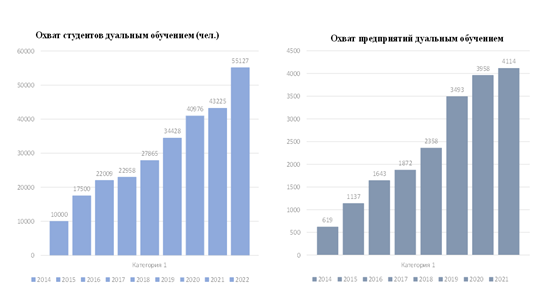
Figure 1.3 - Roadmap for the implementation of dual learning
(in terms of coverage of students and coverage of enterprises) (https://atameken.kz/ru/articles/34263-ucheba-na-proizvodstve--velenie-vremeni)
In the context of regions, the following data on the implementation of dual programs can be cited as examples: in 2020, in the city of Almaty, 750 people studied under the dual system of personnel training and 1720 under educational dual programs. This is only 4% of the total number of college students in Almaty. The main reason is the lack of interest of the vast majority of employers. To resolve this issue in the absence of tax preferences for enterprises participating in dual training, NCE RK "Atameken" proposes to initiate the issue of creating a regulatory mechanism to stimulate employers through the transfer of part of the funds of the state educational order to training enterprises. At the same time, with the assistance of NCE RK "Atameken" in Kazakhstan, good results have been achieved in the creation of production sites. Thus, according to the data for 2020, 314 colleges out of the existing 724 signed contracts with enterprises (Figure 1.4). For 17,500 students, production sites were designated for industrial training.
In the Karaganda region, according to the Regional Chamber of Entrepreneurs, 47 colleges in the region are currently covered by dual education in 100 qualifications, contracts have been concluded with 600 enterprises.
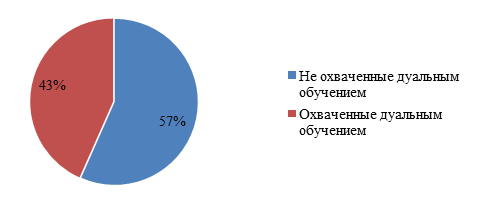
Total: 724 colleges
Of these, contracts with enterprises were concluded - 43% (314)
Figure 1.4 - The ratio of colleges with industrial
sites at enterprises (https://karagandy.atameken.kz/ru/pages/646-about-dual-edu)
In the Kyzylorda and Zhambyl regions, 2 consortiums have been created: the Association of Service and Service Entrepreneurs - the Kyzylorda Industrial-Technical College and Kazphosphate LLP - the Taraz Chemical-Technological College.
The National Report on the State and Development of the Education System of the Republic of Kazakhstan 2020 also indicates that the number of colleges that have introduced the basic principles of dual education is growing every year, while the proportion of students enrolled in dual education remains low. In 2020 535 colleges have implemented the basic principles of dual education (2018 - 486, 2019 - 518) [22].
In general, representatives of colleges note the positive effect of the introduction of dual education, while noting the existing barriers to its effective implementation. These are: low interest of employers in partnership development; problems in the employment of college graduates due to limited vacancies in enterprises; lack of large enterprises in the region, which limits the ability to develop dual education.
To solve these problems, since 2020, work has begun on a targeted basis to reimburse the costs of remuneration to mentors within the framework of per capita financing. It is assumed that this measure will increase the interest of employers in dual training.
Despite the fact that in our country the dual model of education is quite actively used in vocational schools, in universities so far dual education is being introduced pointwise and in the form of elements of dual education.
The country overview and analysis of dual training in the higher education system is practically not presented in the National Report, the websites of the NOBD and the NCE RK "Atameken".
It should also be noted some of the successes achieved by Kazakh universities in the development of dual education. The proposed review uses data from open Internet resources and platforms, the results of a survey and inquiries to universities.
For example, M.Auezov South Kazakhstan University (Auezov SKU) began an experiment on the introduction of dual education in 2016 at the Higher School of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology together with FerrumVtor LLP, Shymkent Temir LLP. The enterprises created conditions for organizing the educational process in production, which provided students with access to the technological process of metal production. The university has a similar experience in implementing dual programs in the areas of "Crop and Livestock" in cooperation with "KAZAGRONOM" LLP, "SMG GREEN HOUSE PROFIT" LLP, "Iftikhari", "Information Technology and Energy" (specialty 5B071800 - Power Engineering) together with " Asia Trafo, which is a large plant in Central Asia for the production of transformer equipment and power transformers, which is part of the leading Kazakh manufacturer of electrical equipment Alageum Electric. Within the framework of dual programs, on-the-job training is conducted in the disciplines proposed by employers. Students' training schedule: 3 days a week - study at the university, 2 days a week - work at the enterprise in positions according to the staffing table. The main indicator of the quality of long-distance educational programs implemented at Auezov SKU is the employment of graduates, which is 15-20% higher than the same indicator for the employment of graduates who have been trained in the traditional form.
Kazakh National Pedagogical University named after Abai (Abai University), which is a leader in the field of higher pedagogical education in Kazakhstan, a major scientific and educational center for methodological support for teacher training, has begun to introduce a new model of curricula for pedagogical specialties, in which a new form of continuous teaching practice is being implemented with the widespread introduction of elements of dual training. For graduate students, blended learning is used - practice throughout the year, providing early employment. In order to improve the professional adaptation of future specialists (teachers) to the needs of the labor market, the Abai University Council of Employers was created at the university.
Karaganda University named after Academician E.A. Buketova has experience in introducing elements of dual education into training programs for engineering specialists in the field of radio electronics and communications, thermal power engineering in partnership with companies in the Karaganda region. Among them are Karaganda Turbomechanical Plant LLP, KARAGANDAENERGOREMONT JSC, Karaganda Energocenter LLP (CHP-1), Representative Offices of National Information Technologies JSC in the Karaganda region, KF ORTPC Kazteleradio, Energoservice LTD LLP, Shakhtinskteploenergo LLP , LLP "Karaganda Zharyk", Association of Individual Entrepreneurs and Legal Entities "Association of Developers and Users of Blockchain Technology "BlockchainKZ", LLP "EPAM Kazakhstan", LLP "Abailyk zhylu zhyyelerі" and others. To improve the quality of training of specialists, the university regularly holds meetings with students, round tables to discuss the issues of updating educational programs, organizing internships in production, training mentors, creating joint production sites, training students on the basis of training centers of partner organizations, training teachers of professional disciplines in methods of developing practical skills of students and organizing practical training training, employers - pedagogical skills for adequate monitoring of students, piloting dual training programs. At the same time, the university has a practice of opening branches of departments on the basis of partner companies, which subsequently play an important role in organizing and conducting student practices, practical trainings and master classes, in organizing on-the-job training. University students sent for practice in partner organizations have the opportunity to conclude a tripartite agreement on professional practice with subsequent employment in the host company. To increase the share of the practical component in the training of specialists, senior students are given the opportunity to work in a company 3-4 days a week, to combine training with professional internships.
Shakarim University also has experience in introducing elements of dual training into the educational process and attracting experienced production practitioners to conduct training sessions, manage graduation theses (projects), which is ensured through the social partnership of the university with such large enterprises, centers and educational institutions as JSC " Semey Engineering", JSC "Semipalatinsk Machine-Building Plant", GLPR "Semey Ormany", LLP "Kondiz", LLP "Corporation" Vostok-Milk", JSC "QazaqAqbas", LLP "Shalabay", LLP "QazaqAstyq Group", KH "Kalikanuly » dairy shop "Aisha", JSC "National Nuclear Center of the Republic of Kazakhstan", State Enterprise "Center for Nuclear Medicine and Oncology of the City of Semey", branch "Nazarbayev Intellectual School of the City of Semey", etc. The purpose of interaction is to ensure the competitiveness and demand for graduates, improve the quality of training specialists, joint research work, co-financing of research projects c and commercialization of research results. Among the dual programs implemented at the university, one can note the educational program "Technical Physics" in partnership with the Republican State Enterprise "National Nuclear Center of the Republic of Kazakhstan", "Forest Resources and Game Science" and "Agronomy" in partnership with the State Forest Natural Reserve "Semey ormany". Such a partnership undoubtedly contributes to the formation of modern design of educational programs, ensures their quality, adaptation to the requirements of employers, and also creates opportunities for successful employment of university graduates.
In the Atyrau University of Oil and Gas named after S. Utebaev (AUNG named after Utebaev), the introduction of dual education has been started since 2015. At present, specialists for the chemical, geological exploration, oil and gas industries, in the field of information systems, automation and production management, industrial energy, and engineering technology are being trained at the S. Utebaev AOGU under the dual system. The partners of AOGU named after Utebaev in dual training are the largest enterprises in the region, including Embamunaigas JSC, Atyrau Oil Refinery LLP, Continent Co LTD LLP, Service Drilling Enterprise KazMunayGas-Drilling LLP, Intergas Central Asia JSC , RSU Department of Ecology for Atyrau Region, Atyrauneftemash LLP, Transtelecom JSC, KAIR Solutions LLP.
The Kazakh-British Technical University is implementing a dual undergraduate program Chemical Technology of Organic Substances, which has passed the international accreditation of IMAREST (Institute of Marine Engineering, Science & Technology, Royal Engineering Council, UK). The program is licensed by the international agency BTEC. The production sites for the implementation of the dual program are oil refineries in Kazakhstan (ANPZ, POCR, PetroKazakhstan), Romania (RomPetrol), etc.
Since 2017, Almaty Management University has entered into agreements with five appraisal companies to implement dual training in the specialty "Assessment". Within the framework of the concluded agreements, students are trained at American Appraisal LLP in the discipline of Economics and Real Estate Management, at American Appriasal, Batagroup, KBS businesscompany, students undergo practical training and internships, including the assessment of objects together with representatives companies. The professional competencies of students are worked out in the process of making decisions at the object of assessment, as well as when performing the necessary calculations for an objective economic assessment of the market value of objects.
In the 2019-2020 academic year, the Economic College of Narxoz University, headed by the NCE of the Republic of Kazakhstan "Atameken", introduced a system of dual education in the specialty 1304000 - "Computer Engineering and Software" into the educational process. The partner-enterprises were the programming school "CodeGuru.be" and the IT partner "IBEC SYSTEMS".
Within the framework of the project "Dual education for industrial automation and robotics in Kazakhstan - DIARKAZ" (ERASMUS + program) by Kazakhstani universities (Innovative Eurasian University, West Kazakhstan Agrarian and Technical University named after Zhangir Khan, Kostanay Engineering and Economic University named after M. Dulatov) the dual training program "Robotic Systems" was developed and the program "Mechatronics and Robotics" was modernized. The draft programs were tested, commented on by the relevant authorities and became part of the regular curriculum; at the Kostanay Engineering and Economic University named after. M. Dulatov, the developed program was successfully accredited and included in the National Register of Educational Programs [27].
In the Karaganda Higher Polytechnic College, 323 students of 10 specialties take part in dual education. All working curricula and educational programs in these specialties are coordinated with partner enterprises (ArcelorMittal Temirtau JSC, KEGOC JSC, QazTehna LLP, Karaganda Turbomechanical Plant LLP, KragandaEnergoCentre LLP, AlmaTelecommunications Kazakhstan JSC, LLP "QazInnovationTechnologies" and others), the number of hours for practical training and work practice has been increased in the curricula, part of the classes are conducted on the basis of enterprises using real production equipment.
Similar work is being carried out at the Electrotechnical College in Semey. Dual education in college covers approximately 25% of the total number of students. For students of dual programs, the hours of practical training in production with the involvement of mentors from enterprises have been increased, the work of mentors is paid from the allocated budget funds, the practical training of students is counted in their seniority.
Despite the fact that, in general, the introduction of dual training has a positive effect, it should be noted that there are barriers to its effective implementation. Among them: low interest of employers in partnership development; problems in the employment of college graduates due to limited vacancies in enterprises; the absence of large enterprises in certain regions, which limits the ability to develop dual education. To solve these problems, since 2020, work has begun in Kazakhstan to reimburse the costs of remuneration to mentors as part of per capita funding. It is assumed that this measure will increase the interest of employers in dual training. In addition, it should be noted that the dual training model is more actively used in technical and vocational training organizations, in universities there is mainly a point introduction of dual training and its elements.